The Difference between PLC and SCADA in Industrial Automation
Two essential components of modern industrial automation and control systems are Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems. While both play crucial roles, understanding their fundamental differences is vital for effectively implementing and leveraging these powerful tools. In today’s highly automated world, industrial processes rely heavily on advanced technologies to ensure efficient operations, data-driven decision-making, and optimal productivity.
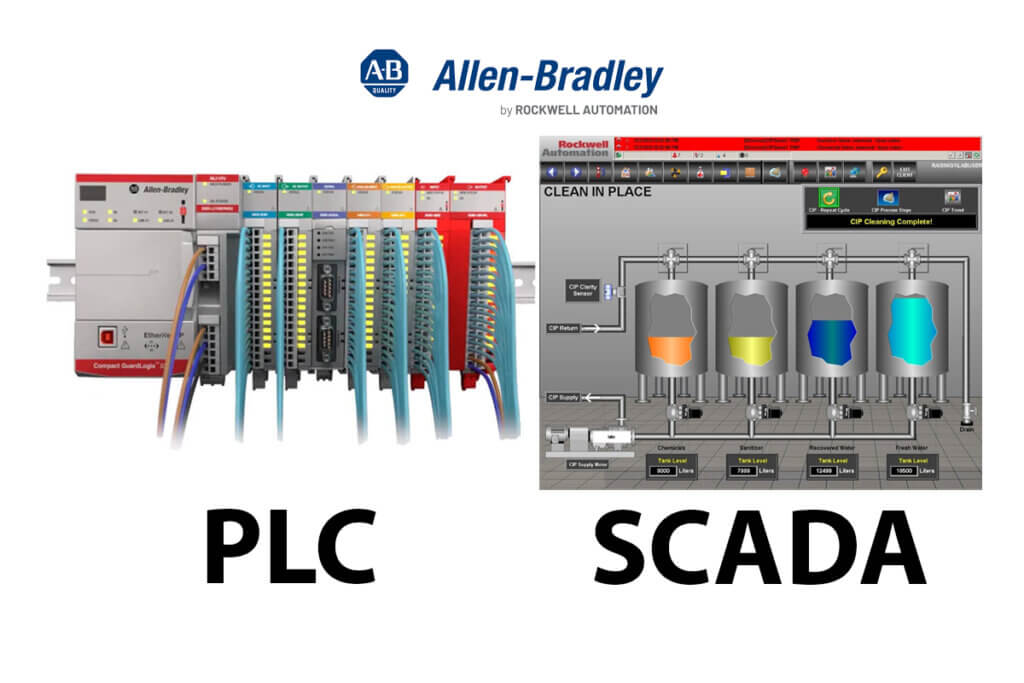

Allen-Bradley PLC and SCADA Systems
What are PLCs and SCADA Systems?
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are specialized industrial computers designed to control and automate various processes and machinery. They are programmed to execute instructions based on input signals from sensors and other field devices. A typical PLC consists of a central processing unit (CPU) that performs the control program, input/output modules for connecting sensors and actuators, and a programming device for writing and uploading the control logic.
PLCs control individual devices, machines, or processes at a localized level. They receive input signals, execute programmed logic, and generate output signals to control actuators, motors, or other equipment. For example, a PLC system might monitor and control a specific assembly line in a manufacturing facility, ensuring that each process step is executed correctly and efficiently.
On the other hand, Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems are comprehensive software solutions designed to monitor and control large-scale industrial processes and operations. SCADA systems collect real-time data from various field devices, such as PLCs, remote terminal units (RTUs), and sensors, and present this information to operators through a centralized human-machine interface (HMI).
Unlike PLCs, which are designed to control individual devices or processes, SCADA systems provide a higher level of supervision and control over an entire system or facility. They act as a central system, enabling operators to monitor and manage multiple processes simultaneously, make informed decisions, and optimize overall operations.
Primary Difference Between PLCs and SCADA
The primary difference between a PLC and a SCADA system lies in their functionality and scope of operation. PLCs are designed to control and execute localized tasks, while SCADA systems are designed to provide supervisory control and data acquisition capabilities over a broader range of processes and equipment.
PLCs operate more granularly, directly controlling individual devices, machines, or processes based on their programmed logic. They receive input signals from sensors or other field devices, process this data through their control program, and generate output signals to control actuators, motors, or other equipment.
SCADA systems operate at a higher level, providing a comprehensive view and control over an entire industrial process or facility. They integrate data from multiple PLCs, sensors, and other field devices, allowing operators to monitor and control the overall system from a central location. SCADA systems are designed to collect, process, and display real-time data from various sources, enabling decision-making and process optimization based on this information.
How do PLCs and SCADA Systems Integrate?
While PLCs and SCADA systems have distinct roles, they often work together in modern industrial automation systems. PLCs are frequently integrated with SCADA systems as data sources and control points, enabling seamless communication and data exchange between these two components.
PLCs execute localized control logic and send data to the SCADA system, which then processes and presents this information to operators. SCADA systems can also send commands and setpoints to PLCs, allowing for remote control and optimization of industrial processes.
This integration enables operators to monitor and control processes from a central location using the SCADA system, while PLCs handle the actual control and execution of specific tasks or equipment. The SCADA system provides a higher-level view and management capabilities, while PLCs handle the low-level control and automation tasks.
Applications of PLCs and SCADA in Various Industries
PLCs and SCADA systems find widespread applications across various industries, where industrial automation and control systems are essential for efficient and reliable operations. Some common applications include:
- Manufacturing and production facilities: PLCs control assembly lines, robotic systems, and production machinery, while SCADA systems monitor and optimize the overall manufacturing process, enabling real-time adjustments and quality control.
- Building automation systems: PLCs control heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC) systems, lighting, and other building systems, while SCADA systems monitor and manage energy consumption, building performance, and environmental conditions.
- Water and wastewater treatment plants: PLCs control pumps, valves, and treatment processes, while SCADA systems monitor water quality, flow rates, and overall plant operations, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
- Oil and gas industry: PLCs control pipeline operations and refinery processes, while SCADA systems monitor and manage the entire pipeline network and refinery operations, enabling efficient distribution and maintenance.
- Power generation and distribution: PLCs control generators, turbines, and substations, while SCADA systems monitor and control the entire power grid, ensuring reliable and efficient energy distribution.
Advantages of Using PLCs and SCADA Systems
Implementing PLCs and SCADA systems in industrial automation offers numerous advantages, including:
- Improved efficiency and productivity: Automating processes and reducing manual interventions increases efficiency, consistency, and productivity, resulting in cost savings and higher output.
- Enhanced data collection and analysis: SCADA systems collect and store vast amounts of data from various sources, enabling detailed analysis, trend identification, and informed decision-making for process optimization and predictive maintenance.
- Remote monitoring and control capabilities: SCADA systems allow operators to monitor and control industrial processes from a central location, reducing the need for on-site personnel and enabling timely interventions in case of issues or emergencies.
- Increased safety and compliance: Automated systems help ensure consistent adherence to safety protocols and industry regulations, minimizing the risk of human errors and potential accidents.
- Scalability and flexibility: PLCs and SCADA systems can be easily expanded or reconfigured to accommodate changing process requirements or facility expansions, providing long-term flexibility and adaptability.
Challenges and Considerations
While PLCs and SCADA systems offer numerous benefits, there are also challenges and considerations to address:
- Cybersecurity concerns in industrial control systems: As PLCs and SCADA systems are often connected to networks and the internet, proper security measures, such as firewalls, access controls, and regular software updates, are crucial to protect against cyber threats and potential breaches.
- System integration and compatibility issues: Ensuring seamless integration and compatibility between different PLCs, SCADA systems, and other components can be challenging, especially when dealing with legacy systems or systems from different vendors.
- Training and skill requirements: Implementing, programming, and maintaining PLCs and SCADA systems requires specialized training and skilled personnel, which can be costly and time-consuming for organizations.
Future Trends in PLCs and SCADA Technologies
The field of industrial automation is continuously evolving, and PLCs and SCADA technologies are adapting to meet new demands and incorporate emerging technologies:
- Cloud-based SCADA solutions: Cloud computing enables the development of cloud-based SCADA systems, offering scalability, remote access, and reduced infrastructure costs, making it easier for organizations to implement and maintain these systems.
- Integration with IoT and Industry 4.0 technologies: PLCs and SCADA systems are integrated with Internet of Things (IoT) devices and technologies, enabling more comprehensive data collection and advanced analytics for predictive maintenance, process optimization, and real-time decision-making.
- Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning: AI and machine learning algorithms are being incorporated into SCADA systems, enabling predictive maintenance, process optimization, and improved decision-making based on pattern recognition and data analysis.
Selecting the Right PLC and SCADA System
Choosing the appropriate PLC and SCADA system for your industrial automation needs is crucial for maximizing efficiency and achieving desired outcomes. Consider the following factors:
- Assessing your industrial process requirements: Evaluate the complexity of your processes, the number of field devices, the level of control and monitoring required, and the level of integration needed between PLCs and SCADA systems.
- Evaluating system scalability and flexibility: Select systems that can easily adapt to future growth or changes in your industrial operations, ensuring long-term viability and avoiding costly replacements or upgrades.
- Considering vendor support and training resources: Partner with reputable vendors that offer comprehensive training, technical support, and regular software updates to ensure your systems remain up-to-date and your personnel are properly trained.
Best Practices for Implementing PLCs and SCADA
To ensure a successful implementation and maximize the benefits of PLCs and SCADA systems, follow these best practices:
- Proper system design and planning: Carefully plan and design your industrial automation system, considering system architecture, communication protocols, integration requirements, and future expansion needs.
- Adhering to industry standards and regulations: Ensure compliance with relevant industry standards, safety regulations, and cybersecurity best practices to maintain a secure and reliable system.
- Regular maintenance and software updates: Implement a regular maintenance schedule and promptly apply software updates and security patches to keep your systems secure, stable, and functioning optimally.
Real-World Case Studies and Success Stories
Numerous companies and organizations across various industries have successfully implemented PLCs and SCADA systems, realizing significant efficiency, productivity, and profitability improvements. Here are a few real-world case studies and success stories:
- A large automotive manufacturer implemented a SCADA system to monitor and control their assembly line processes, resulting in a 20% increase in production output and a 15% reduction in downtime due to improved process visibility and optimization.
- A municipal water treatment plant installed a PLC-based control system and integrated it with a SCADA system. This enabled real-time monitoring of water quality parameters and optimized treatment processes, improving compliance with environmental regulations and reducing costs.
- A large-scale solar power plant utilized PLCs to control and monitor individual solar panels and inverters. At the same time, a SCADA system provided a centralized view of the entire plant’s performance, enabling efficient maintenance and maximizing energy generation through real-time adjustments and predictive maintenance strategies.
Understanding the difference between PLCs and SCADA systems is crucial for effectively leveraging these powerful technologies in industrial automation. By combining the localized control capabilities of PLCs with the comprehensive monitoring and supervisory functions of SCADA systems, businesses can achieve enhanced efficiency, productivity, and profitability while maintaining a high level of safety and compliance. As technology continues to evolve, integrating PLCs and SCADA systems with emerging technologies such as cloud computing, IoT, and artificial intelligence will further revolutionize the realm of industrial automation, enabling more intelligent, data-driven, and optimized operations. Automation Ready Panels can provide your PLC and SCADA using Allen-Bradley components and system. Contact Automation Ready Panels today to discuss your PLC and SCADA implementations.
SHOP NOW
-
Large Process Automation: Panelview 5000, ControlLogix 5580
$21,389.00 Select options -
Small Process Automation: Panelview 5000, ControlLogix 5580
$17,999.00 Select options -
Small Process Automation: ControlLogix 5580, UPS Battery Backup, Cellular Modem
$16,999.00 Select options -
Advanced Automation: Panelview 5000, Safety CompactLogix 5380
$8,499.00 Select options