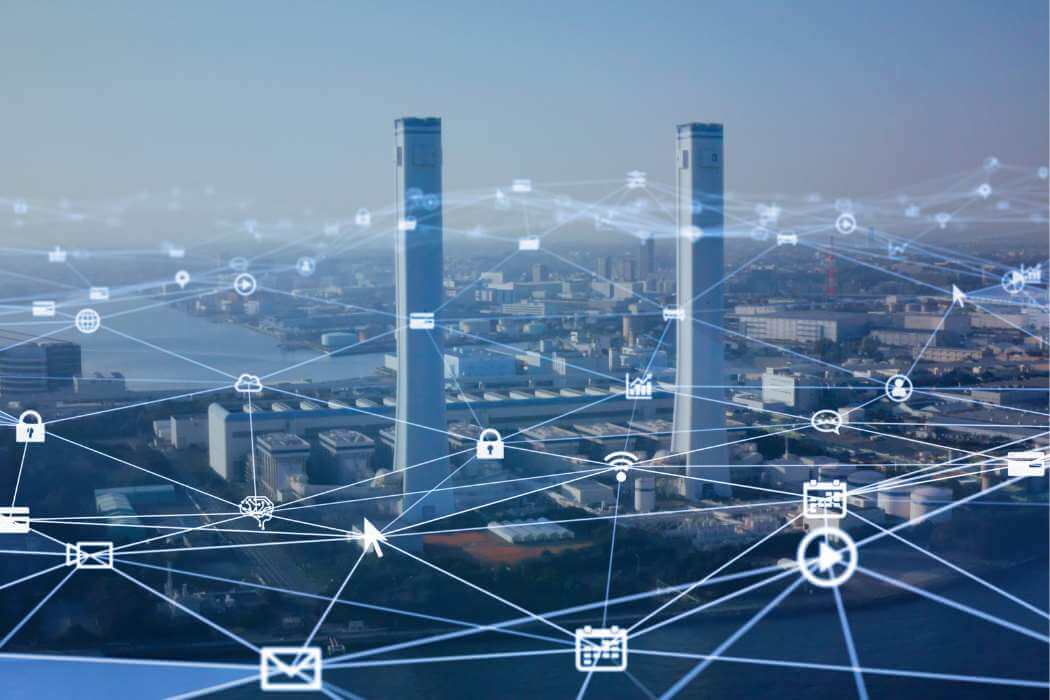
Industrial Revolution: From Industry 1.0 to Industry 4.0
Manufacturing has undergone massive changes since the late 1700s. Picture this: we started with hand tools and have now reached a world where machines can “talk” to each other. Let’s break this journey down into bite-sized pieces.
Business leaders, imagine trying to stay competitive when the rules of the game keep changing. That’s the challenge of industrial revolutions. Each phase shifts how we make products and manage teams.
It started with Industry 1.0, where we traded in handwork for machines powered by water and steam. Then came Industry 2.0, with electricity, and suddenly, we could make more quickly. Next, Industry 3.0 introduced computers into the mix, making things smarter and somewhat hands-off. Now, we’re at Industry 4.0’s doorstep, where the digital and physical worlds blend, aiming to make factories even smarter and more connected.
Understanding these stages isn’t just academic; it’s business-critical. Each revolution opens new doors for efficiency, growth, and innovation. But it’s not just about keeping up—it’s about leveraging these changes for your benefit. Knowing this history is more than trivia; it’s insight that could shape the future of your business in this fast-paced manufacturing saga.
The Beginnings of Industrial Revolution: Industry 1.0
The first wave of industrial change, known as Industry 1.0, profoundly changed the world. It was more than just a change in how things were made; it was a change in how people lived.
Machines started to take over work that was done by hand. The rise of steam power defined this era. The power of steam made it possible to produce more goods than ever before and changed how we got things from one place to another.
This shift had big effects on society. People’s quality of life began to get better, and more people were born as a result. Many people moved to cities looking for work, which led to overcrowded living conditions and social challenges.
In this time of great change, some inventions really stood out. Take James Watt’s steam engine, for example. It made a huge difference in transportation and manufacturing. The spinning jenny, created by James Hargreaves, changed the textile industry entirely.
In summary, Industry 1.0 was a time of great advancements. It set the stage for future growth and set in motion the wheels of industrial progress that we are continuing today.
The Dawn of Mass Production: Industry 2.0
With Industry 2.0, we saw the start of something huge: mass production. This was the second big shake-up in industry, fueling economies and changing the game in manufacturing.
This era was all about moving from making things by hand to making them fast and in large numbers, thanks to assembly lines. This step allowed products to be made cheaper and faster than ever before. Electricity took over from steam, powering up factories like never before and letting them run longer and more efficiently.
This shift is still shaping how we make things today. Because of mass production, more people could afford products, which helped grow the middle class. This period also set the stage for the kind of automation and digital work we see now.
This time also brought us game-changing inventions. The telephone, the light bulb, and the automobile are just a few examples. These weren’t just new gadgets; they created whole new industries and jobs.
In short, Industry 2.0 was when we really started to speed up and scale up, laying the groundwork for the advanced technology and manufacturing systems we use today.
The Digital Revolution: Industry 3.0
The third great change in the manufacturing world, known as Industry 3.0, brought us into the digital age. This era followed the invention of machines and the start of mass production, adding a new layer: advanced technology.
In the late 20th century, everything began to change rapidly with the introduction of automation and computers. These tools allowed factories to run with less manual work, increasing the speed and amount of products they could create. The internet and digitalization – turning information into a format computers can read – also transformed how businesses manage information.
The impact of Industry 3.0 was huge. It reshaped old industries and created new ones, like IT and digital startups. This period saw personal computers become common, the use of programmable logic controllers (devices that automate industrial processes), and the birth of the internet, changing how we communicate and do business.
Industry 3.0 was a turning point. It made technology a fundamental part of how we live and work, setting the stage for all the modern tech we rely on today.
The Dawn of Smart Technology: Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is like the new age of smart technology in manufacturing. The latest revolution builds on what started with automation and computers on the production floor. Now, we’re looking at a wave of advanced tech that’s making everything more connected and efficient.
At the heart of Industry 4.0 are concepts like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), which let machines get smarter on their own. Then there’s the Internet of Things (IoT), which connects devices to talk to each other and share information. And let’s not forget Big Data – this is all about crunching huge amounts of information to make smarter decisions.
This shift is huge – it’s changing how we’ve always done things across different fields, making processes more digital and efficient. It’s not just about doing things faster; it’s also about being more flexible and eco-friendly in how we work.
What’s next? We’re likely to see an even closer blend of digital and physical systems, with real-time communication and smarter use of resources. As more industries jump on board, we’re looking at changes that could redefine not just manufacturing but all kinds of services and industries, tapping into the full scope of human creativity and innovation.
Comparisons and Differences between Industry 1.0 to 4.0
The story of industrial progress is fascinating, stretching from the age of steam to the era of smart technology. Let’s explore how these stages differ from one another.
Industry 1.0 started it all by moving from handwork to machines, with steam and water power leading the charge. Then, Industry 2.0 introduced electricity, which allowed for the assembly line method of production, drastically boosting the speed and scale at which products could be made.
The third phase, Industry 3.0, brought in the era of automation. Electronics and information technology made manufacturing even faster and more precise. Now, we’re living through Industry 4.0, where everything is becoming connected. This digital industrial revolution uses smart systems and the Internet of Things to create factories that almost think for themselves.
Each transition has been marked by new ways to produce and new technologies, from steam engines to electricity, then to computers, and now to interconnected digital networks. These changes have reshaped how we make things and our economies, job markets, and daily lives.
The Future Beyond Industry 4.0
The buzz around Industry 4.0 is just the beginning. What comes next? We’re looking toward Industry 5.0. This isn’t just about machines; it’s about bringing human creativity back into the mix with advanced AI. Imagine people and robots working side by side, enhancing each other’s work.
The future also looks green. Sustainability isn’t just good for the planet; it’s smart business. Future factories will aim to cut waste and reuse resources, helping to create a cleaner, more efficient way of making things. And then there’s the blending of worlds. The next revolution will see even more of a merge between our physical and digital spaces. Businesses will operate in new ways, with a seamless flow between the real and the virtual. It’s all setting the stage for a big change, one that combines technology and human imagination in ways we’ve just started to imagine.
Conclusion
The journey from the gritty beginnings of Industry 1.0 to the advanced digital landscape of Industry 4.0 has reshaped our world profoundly. Starting with steam and water power, moving to electricity and the assembly line, then on to computerization, and now into the realm of smart, self-learning systems, each industrial leap has left an indelible mark on how we live and work.
Staying in step with these changes is crucial for any business. Falling behind could mean getting left out of the next big wave of innovation. But this journey isn’t just about keeping up—it’s about being connected.
Today’s world is more interconnected than ever, and this connectivity drives new discoveries and their adoption across the globe. The industrial revolutions show us that progress isn’t just linear—it’s a constant cycle of innovation, impact, and evolution. As we look forward, the story of the industry is far from over. It’s just getting ready for its next chapter.
At Automation Ready Panels, we understand industry trends and adapt as needed. Contact us for any of your PLC control panel needs or automation requirements.
SHOP NOW
-
Large Process Automation: Panelview 5000, ControlLogix 5580
$21,389.00 Select options -
Small Process Automation: Panelview 5000, ControlLogix 5580
$17,999.00 Select options -
Small Process Automation: ControlLogix 5580, UPS Battery Backup, Cellular Modem
$16,999.00 Select options -
Advanced Automation: Panelview 5000, Safety CompactLogix 5380
$8,499.00 Select options