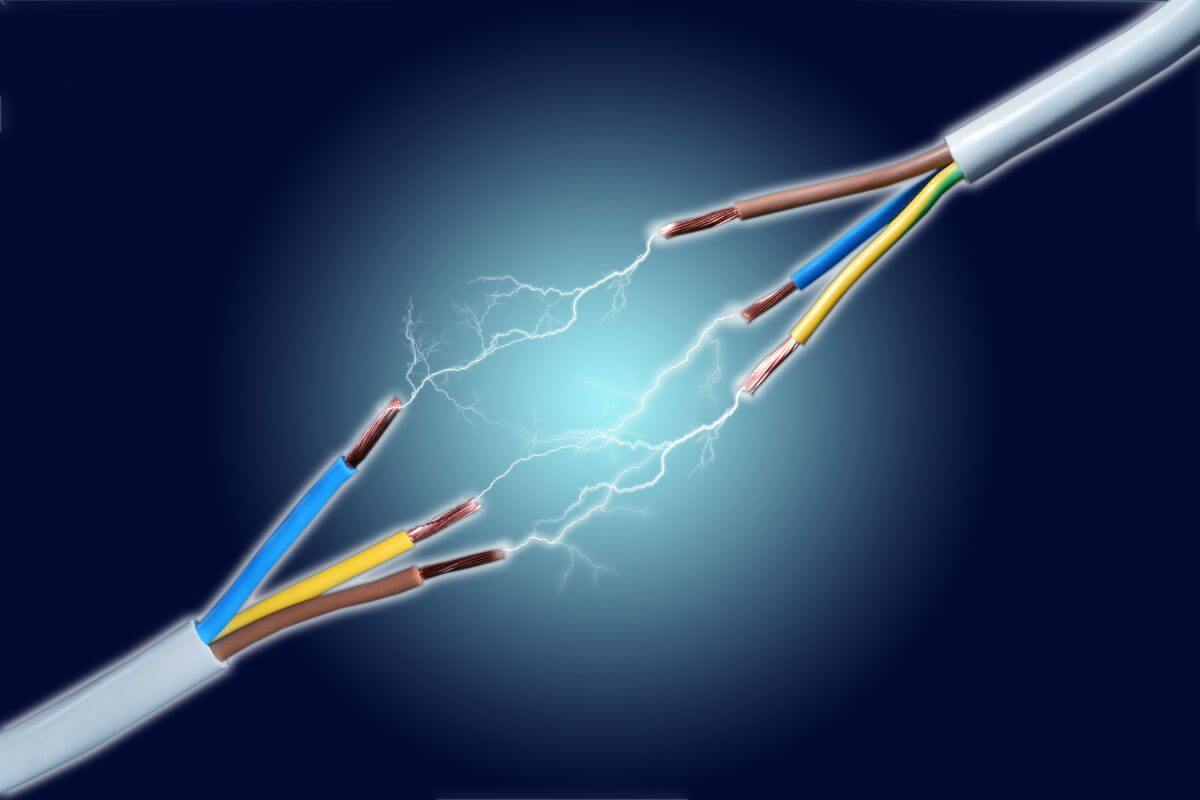
Single Phase vs Three Phase Power in Simple Terms
When it comes to electric power, it’s essentially about how swiftly electrical energy moves within a circuit.
At the heart of many manufacturing processes lies the need for reliable electrical power. But there’s more to it than just “power.” The way this power is delivered – either as single phase or three phase – matters immensely. Without an understanding of these power phases, you might be leaving efficiency gains and cost savings on the table. Not to mention, it’s pivotal for ensuring safety standards in your facilities.
Around the globe, both single phase and three phase power are employed in homes, businesses, and industrial settings. But here’s the catch: they’re not interchangeable. Each has its unique advantages and best-use scenarios. Making uninformed decisions could lead to less-than-optimal operations, higher bills, and even potential safety risks.
We’re here to demystify this for you. This article is tailored for business decision-makers like you, stripping away the technical overload. We’ll compare single phase and three phase power in easy-to-grasp terms, highlighting their differences and guiding you on when to use each. So, sit tight and allow us to navigate you through the pivotal elements of electric power phases, ensuring you’re well-equipped to make informed, beneficial decisions for your manufacturing operations.
Understanding the Basics of Electricity
Electricity isn’t just the flick of a switch or the light in our rooms. At its core, it’s a fundamental force of nature, driving a multitude of processes, especially in manufacturing.
The Essence of Electricity
Think of electricity as the grand movement of tiny particles known as electrons. This movement, from one point to another, is the result of a presence and transfer of electric charge. In more relatable terms, it’s like water flowing in a river due to a driving force behind it.
Decoding the Key Elements
When discussing electricity, three terms often pop up – current, voltage, and resistance.
- Voltage is akin to the pressure pushing the water (or in this case, electric charge) forward.
- Current represents the actual flow of this water – the movement of our charged electrons.
- Resistance, on the other hand, can be likened to obstacles in the river that hinder or slow down this flow.
Electricity in Action
It’s hard to imagine a world without electricity. From illuminating our homes and powering everyday gadgets to driving critical manufacturing processes and breakthroughs in medical science, its influence is omnipresent. For business decision-makers in manufacturing, appreciating this essence can help optimize operations, boost efficiency, and ensure safety.
As we continue our journey through the digital age, it’s electricity that remains the unsung hero, enabling advancements, innovations, and conveniences in countless ways, from the mundane to the monumental.
Power Phases Explained
Power Phases might sound technical, but they’re fundamental for those in manufacturing. Let’s simplify this concept for those steering the ship in industries.
What are Power Phases?
In the realm of electricity, think of power phases as the rhythm or timing of electrical currents as they flow. It’s like coordinating dancers on a stage—each one performs a move at a specific time to create a cohesive performance. These phases ensure electricity is delivered smoothly, securely, and efficiently.
Why Care About Power Phases?
These rhythmic flows keep everything in balance. They maintain stable electrical loads, ward off erratic power spikes, and enhance energy efficiency. Getting this rhythm wrong? That can spell trouble, from machinery breakdowns to excessive power consumption and even potential safety risks.
Single vs. Three Phase Power:
- Single Phase Power: Picture a duet on a stage—two dancers (or wires) moving in sync. This is what powers your home appliances and is adequate for areas with modest power needs.
- Three Phase Power: Now, imagine a trio, each dancer starting their routine at a different beat, ensuring there’s always one performing. This system, with its trio of wires, meets the needs of power-hungry commercial and industrial sectors. The beauty of it? It guarantees a never-ending, steady stream of energy, invaluable for operations that can’t afford a break in power.
Understanding Single Phase Power
Delving into electrical concepts can be overwhelming but for decision-makers in manufacturing and business, having a grasp on Single Phase Power is essential. Let’s break it down.
What is Single Phase Power?
Imagine a duo playing the piano, where both players strike the keys in perfect harmony, producing a synchronized melody. Single Phase Power works similarly. Here, we have two “players” or conductors— one actively transmitting power while the other remains neutral. The result? A power supply where all voltages rise and fall in harmony, aptly named “single phase”.
Where is it Used?
If you’ve ever wondered what powers your home lights, the heater in your room, or your kitchen appliances like the refrigerator and microwave— it’s Single Phase Power. Beyond the home, this power system also finds use in commercial spaces and some smaller-scale industrial setups, even supporting automated controls like Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs).
Why Choose Single Phase Power?
- Simplicity: Its straightforward nature makes it easily comprehensible and manageable.
- Cost-Effective: Distributing Single Phase Power is lighter on the wallet compared to the more complex Three Phase Power.
Limitations to Consider
Every system has its constraints. The major limitation of Single Phase Power is its inefficiency in fueling extensive industrial machinery or robust motors. This is mainly due to the pulsing manner in which it delivers power. While it’s great for residential and some commercial settings, larger facilities often lean towards Three Phase Power for optimum efficiency.
Three Phase Power Unveiled: A Primer for Manufacturing Executives
In the expansive world of power distribution, Three Phase Power emerges as a formidable player, especially in sectors demanding uninterrupted power. But what exactly is it, and why is it so widely adopted in large-scale operations? Let’s delve in.
What is Three Phase Power?
Think of a trio of musicians, each playing a distinct note, yet together producing a harmonious and constant tune. Three Phase Power is analogous to this. It employs three conductors, each transmitting power in a sequence, ensuring a perpetual and stable flow. This means that the power stream never really ‘takes a break’, bridging the power gaps close to nil.
Where Do We See It in Action?
When it comes to fueling immense machinery, robust equipment, or facilities like expansive data centers, Three Phase Power takes center stage. It’s the power backbone for major industrial sites, manufacturing plants, and large commercial edifices. One crucial application is in the Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) systems, showcasing its robustness and reliability in controlling intricate industrial operations.
Benefits of Opting for Three Phase Power:
- Consistency: The unique three-conductor system ensures a steady power flow, vital for industrial applications.
- Enhanced Load Capacity: Perfect for heavy-duty operations that single-phase power simply can’t handle.
- Higher Efficiency: This system boasts of superior energy efficiency, especially when compared to its single-phase counterpart.
Points to Ponder
However, like all things, Three Phase Power isn’t devoid of challenges. Its installation comes at a heftier price tag, mainly due to the triple-conductor setup. Yet, when we balance the scales, the high initial investment is often justified by its unparalleled performance and reliability in demanding settings.
Single Phase vs. Three Phase Power
Navigating the realms of electrical power can seem daunting. For industry leaders, understanding the distinctions between Single Phase and Three Phase Power is vital for efficient operations. Let’s simplify this.
Single Phase Power At A Glance
- Design: Utilizes one sinusoidal voltage, making it straightforward and uncomplicated.
- Applications: Ideal for homes and small-scale commercial endeavors. Powers your household fans, refrigerators, and computers.
- Efficiency: Given its non-uniform power delivery, it isn’t the best fit for heavy machinery.
- Cost: Installation is generally more affordable due to its simplicity.
Three Phase Power In Focus:
- Design: Employs three sinusoidal voltage levels, staggered 120 degrees apart, ensuring a balanced and consistent power delivery.
- Applications: The go-to choice for industries, manufacturing plants, and expansive commercial spaces. Powers heavy-duty machinery and works seamlessly with PLCs to oversee intricate industrial operations.
- Efficiency: Thanks to its uniform power output, it’s tailor-made for substantial power needs, making operations smoother and more efficient.
- Cost: The initial investment is heftier, considering its intricate design. Yet, its efficiency often results in long-term power and cost savings, especially in large-scale applications.
Choosing between Single Phase and Three Phase Power boils down to the specific needs and scale of your operations. For modest power requirements and budget-conscious projects, Single Phase is a viable choice. However, for enterprises demanding relentless, efficient power, the initial investment in Three Phase Power is often a wise, long-term decision.
Wrapping It Up: Making the Right Power Choice for Your Operations
Distinguishing between Single Phase and Three Phase power systems isn’t just a technical exercise—it’s pivotal for driving efficiency, especially in areas like industrial automation and managing control panels.
To recap the insights shared:
- Single Phase Power: A fit for homes and small-scale ventures, it’s simpler and more budget-friendly but might not offer the heft and efficiency required for more demanding tasks.
- Three Phase Power: The powerhouse for industries, it’s designed to cater to heavy-duty requirements, delivering consistent power and maximizing efficiency—even if it demands a higher initial investment.
The choice between these two will significantly shape your operational effectiveness and bottom line. It’s akin to choosing between a regular car and a heavy-duty truck; both have their places and purposes.
Keep in mind the trio of factors: your specific needs, budgetary constraints, and the desired efficiency. Weighing these judiciously ensures you harness the power that’s just right for you, positioning you for both immediate success and future growth.
SHOP NOW
-
Large Process Automation: Panelview 5000, ControlLogix 5580
$21,389.00 Select options -
Small Process Automation: Panelview 5000, ControlLogix 5580
$17,999.00 Select options -
Small Process Automation: ControlLogix 5580, UPS Battery Backup, Cellular Modem
$16,999.00 Select options -
Advanced Automation: Panelview 5000, Safety CompactLogix 5380
$8,499.00 Select options